5. Sets and Maps¶
In the last chapter we studied sequences which are used to keep track of lists of things where duplicate values are allowed. For instance, there can be two sixes in a sequence or list of integers. In this chapter we look at sets where duplicate values are not allowed. After examining sets we’ll move on to talk about maps. Maps may also be called dictionaries or hash tables.
The term hash table actually suggests an implementation of a set or map. The primary focus of this chapter is in understanding hashing. Hashing is a very important concept in Computer Science because it is a very efficient method of searching for a value. To begin the chapter we’ll motivate our interest in hashing, then we’ll develop a hashing algorithm for finding values in a set. We’ll also apply hashing to the building of sets and maps. Then we’ll look at an important technique that uses hashing called memoization and we’ll apply that technique to a couple of problems.
5.1. The HashSet Datatype¶
You can download HashSet datatype implementation here. The implementation is partial. The remainder of the set implementation is left as an exercise for the reader.
1#################################################################################
2# HashSet.py - A hashtable implementation of a set datatype.
3#################################################################################
4# To complete this implementation you must complete the code for all methods that
5# currently have a "pass" in them. Consult the documentation for these methods
6# to see what they should return. Many of these methods can be implemented
7# by calling other supporting methods, so make sure you don't write more
8# code than necessary. Many methods take exactly one line of code to implement.
9# The test main function at the bottom should completely run passing all tests
10# once you have implemented the methods here. The test main function is not
11# intended to completely test the entire class though. You have to write
12# additional tests to throroughly test the HashSet class.
13
14class HashSet:
15 class __Placeholder:
16 def __init__(self):
17 pass
18
19 def __eq__(self,other):
20 return False
21
22 def __add(item,items):
23 idx = hash(item) % len(items)
24 loc = -1
25
26 while items[idx] != None:
27 if items[idx] == item:
28 # item already in set
29 return False
30
31 if loc < 0 and type(items[idx]) == HashSet.__Placeholder:
32 loc = idx
33
34 idx = (idx + 1) % len(items)
35
36 if loc < 0:
37 loc = idx
38
39 items[loc] = item
40
41 return True
42
43 def __remove(item,items):
44 idx = hash(item) % len(items)
45
46 while items[idx] != None:
47 if items[idx] == item:
48 nextIdx = (idx + 1) % len(items)
49 if items[nextIdx] == None:
50 items[idx] = None
51 else:
52 items[idx] = HashSet.__Placeholder()
53 return True
54
55 idx = (idx + 1) % len(items)
56
57 return False
58
59 def __rehash(oldList, newList):
60 for x in oldList:
61 if x != None and type(x) != HashSet.__Placeholder:
62 HashSet.__add(x,newList)
63
64 return newList
65
66 def __init__(self,contents=[]):
67 self.items = [None] * 10
68 self.numItems = 0
69
70 for item in contents:
71 self.add(item)
72
73 def __str__(self):
74 pass
75
76 def __iter__(self):
77 for i in range(len(self.items)):
78 if self.items[i] != None and type(self.items[i]) != HashSet.__Placeholder:
79 yield self.items[i]
80
81 # Following are the mutator set methods
82 def add(self, item):
83 if HashSet.__add(item,self.items):
84 self.numItems += 1
85 load = self.numItems / len(self.items)
86 if load >= 0.75:
87 self.items = HashSet.__rehash(self.items,[None]*2*len(self.items))
88 def remove(self, item):
89 if HashSet.__remove(item,self.items):
90 self.numItems -= 1
91 load = max(self.numItems, 10) / len(self.items)
92 if load <= 0.25:
93 self.items = HashSet.__rehash(self.items,[None]*int(len(self.items)/2))
94 else:
95 raise KeyError("Item not in HashSet")
96
97 def discard(self, item):
98 pass
99
100 def pop(self):
101 pass
102
103 def clear(self):
104 pass
105
106 def update(self, other):
107 pass
108
109 def intersection_update(self, other):
110 pass
111
112 def difference_update(self, other):
113 for item in other:
114 self.discard(item)
115
116 def symmetric_difference_update(self, other):
117 pass
118
119 # Following are the accessor methods for the HashSet
120 def __len__(self):
121 pass
122
123 def __contains__(self, item):
124 idx = hash(item) % len(self.items)
125 while self.items[idx] != None:
126 if self.items[idx] == item:
127 return True
128
129 idx = (idx + 1) % len(self.items)
130
131 return False
132
133 # One extra method for use with the HashMap class. This method is not needed in the
134 # HashSet implementation, but it is used by the HashMap implementation.
135 def __getitem__(self, item):
136 pass
137
138 def not__contains__(self, item):
139 pass
140
141 def isdisjoint(self, other):
142 pass
143
144
145 def issubset(self, other):
146 pass
147
148
149 def issuperset(self, other):
150 pass
151
152 def union(self, other):
153 pass
154
155 def intersection(self, other):
156 pass
157 #done
158 def difference(self, other):
159 pass
160
161 def symmetric_difference(self, other):
162 pass
163
164 def copy(self):
165 pass
166
167 # Operator Definitions
168 def __or__(self, other):
169 pass
170
171 def __and__(self,other):
172 pass
173
174 def __sub__(self,other):
175 pass
176
177 def __xor__(self,other):
178 pass
179
180 def __ior__(self,other):
181 pass
182
183 def __iand__(self,other):
184 pass
185
186 def __ixor(self,other):
187 pass
188
189 def __le__(self,other):
190 pass
191
192 def __lt__(self,other):
193 pass
194
195 def __ge__(self,other):
196 pass
197
198 def __gt__(self,other):
199 pass
200
201 def __eq__(self,other):
202 pass
203
204
205
206def main():
207 s = HashSet(list(range(100)))
208
209 t = HashSet(list(range(10,20)))
210
211 u = HashSet(list(range(10,20)))
212
213 if len(t) == len(u) and len(t) == 10:
214 print("Test 1 Passed")
215 else:
216 print("Test 1 Failed")
217
218 s.intersection_update(t)
219
220 if len(s) == 10:
221 print("Test 2 Passed")
222 else:
223 print("Test 2 Failed")
224
225 s = HashSet(list(range(100)))
226
227 t.update(s)
228
229 if len(s) == len(t):
230 print("Test 3 Passed")
231 else:
232 print("Test 3 Failed")
233
234 t.clear()
235 t.update(u)
236
237 if len(t) == len(u):
238 print("Test 4 Passed")
239 else:
240 print("Test 4 Failed")
241
242 s.difference_update(t)
243
244 test5Passed = True
245 test6Passed = True
246
247 for x in range(1,10):
248 if x in s:
249 pass
250 else:
251 test5Passed = False
252 print("Test 5 Failed on",x)
253
254 if x not in s:
255 test6Passed = False
256 print("Test 6 Failed on",x)
257
258 if test5Passed:
259 print("Test 5 Passed")
260
261 if test6Passed:
262 print("Test 6 Passed")
263
264
265 test7Passed = True
266 test8Passed = True
267
268 for x in range(20,100):
269 if x in s:
270 pass
271 else:
272 test7Passed = False
273 print("Test 7 Failed on",x)
274
275 if x not in s:
276 test8Passed = False
277 print("Test 8 Failed on",x)
278
279 if test7Passed:
280 print("Test 7 Passed")
281
282 if test8Passed:
283 print("Test 8 Passed")
284
285 x = HashSet(["a","b","c","d","e","f","g","h","i","j","k"])
286
287 y = HashSet(["c","d","e","l","m","n"])
288
289 z = x.difference(y)
290
291 if len(z) == 8:
292 print("Test 9 Passed")
293 else:
294 print("Test 9 Failed")
295
296 test10Passed = True
297
298 for item in z:
299 if item not in ["a","b","f","g","h","i","j","k"]:
300 test10Passed = False
301 print("Test 10 Failed on", x)
302
303 if test10Passed:
304 print("Test 10 Passed")
305
306 if z.issubset(x):
307 print("Test 11 Passed")
308 else:
309 print("Test 11 Failed")
310
311 if x.issuperset(z):
312 print("Test 12 Passed")
313 else:
314 print("Test 12 Failed")
315
316 if z == y:
317 print("Test 13 Failed")
318 else:
319 print("Test 13 Passed")
320
321 if z == z:
322 print("Test 14 Passed")
323 else:
324 print("Test 14 Failed")
325
326 r = z.copy()
327
328 if r == z:
329 print("Test 15 Passed")
330 else:
331 print("Test 15 Failed")
332
333 for item in range(50):
334 z.add(item)
335
336 for item in range(50):
337 z.discard(item)
338
339 if r == z:
340 print("Test 16 Passed")
341 else:
342 print("Test 16 Failed")
343
344 for item in range(50):
345 z.add(item)
346
347 for item in range(50):
348 z.remove(item)
349
350 if r == z:
351 print("Test 17 Passed")
352 else:
353 print("Test 17 Failed")
354
355
356if __name__ == "__main__":
357 main()
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
5.2. The HashMap Datatype¶
You can download HashMap datatype implementation here. The implementation is partial. The remainder of the set implementation is left as an exercise for the reader. The HashMap datatype requires a module called hashset.py containing the HashSet datatype.
1import hashset
2
3class HashMap:
4 class __KVPair:
5 def __init__(self,key,value):
6 self.key = key
7 self.value = value
8
9 def __eq__(self,other):
10 if type(self) != type(other):
11 return False
12
13 return self.key == other.key
14
15 def getKey(self):
16 return self.key
17
18 def getValue(self):
19 return self.value
20
21 def __hash__(self):
22 return hash(self.key)
23
24 def __init__(self):
25 self.hSet = hashset.HashSet()
26
27 def __len__(self):
28 return len(self.hSet)
29
30 def __contains__(self,item):
31 return HashMap.__KVPair(item,None) in self.hSet
32
33 def not__contains__(self,item):
34 return item not in self.hSet
35
36 def __setitem__(self,key,value):
37 self.hSet.add(HashMap.__KVPair(key,value))
38
39 def __getitem__(self,key):
40 if HashMap.__KVPair(key,None) in self.hSet:
41 val = self.hSet[HashMap.__KVPair(key,None)].getValue()
42 return val
43
44 raise KeyError("Key " + str(key) + " not in HashMap")
45
46 def get(self,key,default=None):
47 if HashMap.__KVPair(key,None) in self.hSet:
48 return self.hSet[HashMap.__KVPair(key,None)].getValue()
49 else:
50 return default
51
52 def __delitem__(self,key):
53 if HashMap.__KVPair(key,None) in self.hSet:
54 self.hSet.remove(key)
55 else:
56 raise KeyError("Key " + key + " not in HashMap")
57
58 def items(self):
59 result = []
60 for x in self.hSet:
61 result.append((x.getKey(),x.getValue()))
62 return result
63
64 def keys(self):
65 result = []
66 for x in self.hSet:
67 result.append(x.getKey())
68 return result
69
70 def values(self):
71 result = []
72 for x in self.hSet:
73 result.append(x.getValue())
74 return result
75
76 def pop(self, key):
77 if HashMap.__KVPair(key,None) in self.hSet:
78 item = self.hSet[key]
79 return item.getValue()
80 else:
81 raise KeyError("Key " + key + " not in HashMap")
82
83 def popitem(self):
84 item = self.hSet.pop()
85 return (item.getKey(),item.getValue())
86
87 def setdefault(self):
88 pass
89
90 def update(self,other):
91 pass
92
93 def clear(self):
94 pass
95
96 def copy(self):
97 pass
98
99 def __iter__(self):
100 for x in self.hSet:
101 yield x.getKey()
102
103def main():
104 d = HashMap()
105 print(len(d))
106 d["dog"] = "cat"
107 d["batman"] = "joker"
108 d["superman"] = "lex luther"
109 for key in d:
110 print(key)
111
112 for key in d:
113 print(key,d[key])
114
115 d["dog"] = "skunk"
116
117 print(d.popitem())
118
119 for key in d:
120 print(key,d[key])
121
122if __name__ == "__main__":
123 main()
5.3. Sudoku Puzzles¶
Here are six sudoku puzzles that can be solved using the sudoku solver rules that are discussed in this chapter.
5.4. Figures from Text¶
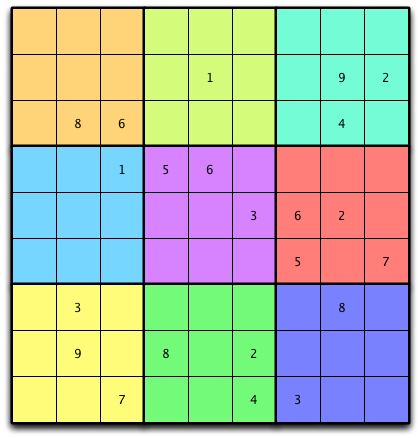
Fig. 1: A Sudoku Puzzle¶
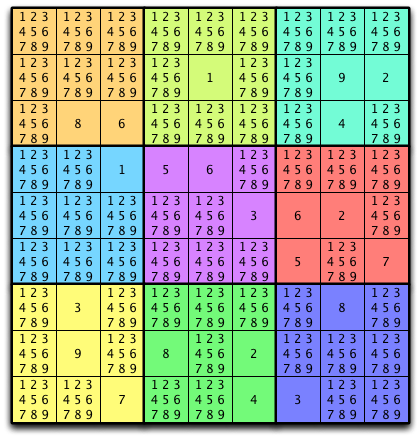
Fig. 2: Annotated Sudoku Puzzle¶
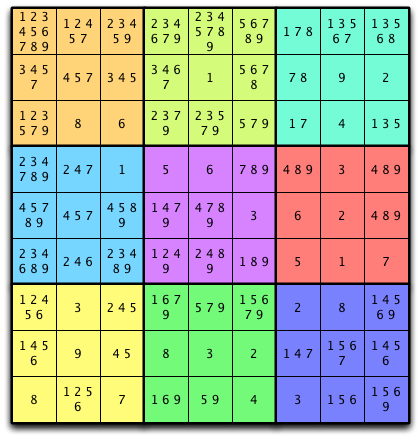
Fig. 3: Sudoku Puzzle After One Pass¶
Operation |
Complexity |
Usage |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Set Creation |
O(1) |
s=set([iterable]) |
Calls the set constructor to create a set. Iterable is an optional initial contents in which case we have O(n) complexity. |
Set Creation |
O(1) |
s=frozenset([iterable]) |
Calls the frozenset constructor for immutable set objects to create a frozenset object. |
Cardinality |
O(1) |
len(s) |
The number of elements in s is returned. |
Membership |
O(1) |
e in s |
Returns True if e is in s and False otherwise. |
non-Membership |
O(1) |
e not in s |
Returns True if e is not in s and False otherwise. |
Disjoint |
O(n) |
s.isdisjoint(t) |
Returns True if s and t share no elements, and False otherwise. |
Subset |
O(n) |
s.issubset(t) |
Returns True if s is a subset of t, and False otherwise. |
Superset |
O(n) |
s.issuperset(t) |
Returns True if s is a superset of t and False otherwise. |
Union |
O(n) |
s.union(t) |
Returns a new set which contains all elements in s and t. |
Intersection |
O(n) |
s.intersection(t) |
Returns a new set which contains only the elements in both s and t. |
Set Difference |
O(n) |
s.difference(t) |
Returns a new set which contains the elements of s that are not in t. |
Symmetric Difference |
O(n) |
s.symmetric_diff- erence(t) |
Returns a new set which contains s.difference(t).union(t.difference(s)). |
Set Copy |
O(n) |
s.copy() |
Returns a shallow copy of s. |

Fig. 4: Set and Frozen Set Operations¶
Operation |
Complexity |
Usage |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Union |
O(n) |
s.update(t) |
Adds the contents of t to s. |
Intersection |
O(n) |
s.intersection_update(t) |
Updates s to contain only the intersection of the elements from s and t. |
Set Difference |
O(n) |
s.difference_update(t) |
Subtracts from s the elements of t. |
Symmetric Difference |
O(n) |
s.symmetric_diff- erence_update(t) |
Updates s with the symmetric difference of s and t. |
Add |
O(1) |
s.add(e) |
Add the element e to the set s. |
Remove |
O(1) |
s.remove(e) |
Remove the element e from the set s. This raises KeyError if e does not exist in s. |
Discard |
O(1) |
s.discard(e) |
Remove the element e if it exists in s and ignore it otherwise. |
Pop |
O(1) |
s.pop() |
Remove an arbitrary element of s. |
Clear |
O(1) |
s.clear() |
Remove all the elements of s leaving the set empty. |

Fig. 5: Mutable Set Operations¶
Operation |
Complexity |
Usage |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Dictionary Creation |
O(1) |
d = {[iterable]} |
Calls the constructor to create a dictionary. Iterable is an optional initial contents in which case it is O(n) complexity. |
Size |
O(1) |
len(d) |
The number of key/value pairs in the dictionary. |
Membership |
O(1) |
k in d |
Returns True if k is a key in d and False otherwise. |
non-Membership |
O(1) |
k not in d |
Returns True if k is not a key in d and False otherwise. |
Add |
O(1) |
d[k] = v |
Adds (k,v) as a key/value pair in d. |
Lookup |
O(1) |
d[k] |
Returns the value associated with the key, k. A KeyError exception is raised if k is not in d. |
Lookup |
O(1) |
d.get(k[,default]) |
Returns v for the key/value pair (k,v). If k is not in d returns default or None if not specified. |
Remove Key/Value Pair |
O(1) |
del d[k] |
Removes the (k,v) key value pair from d. Raises KeyError if k is not in d. |
Items |
O(1) |
d.items() |
Returns a view of the key/value pairs in d. The view updates as d changes. |
Keys |
O(1) |
d.keys() |
Returns a view of the keys in d. The view updates as d changes. |
Values |
O(1) |
d.values() |
Returns a view of the values in d. The view updates as d changes. |
Pop |
O(1) |
d.pop(k) |
Returns the value associated with key k and deletes the item. Raises KeyError if k is not in d. |
Pop Item |
O(1) |
d.popitem() |
Return an abritrary key/value pair, (k,v), from d. |
Set Default |
O(1) |
d.setdefault(k[,default]) |
Sets k as a key in d and maps k to default or None if not specified. |
Update |
O(n) |
d.update(e) |
Updates the dictionary, d, with the contents of dictionary e. |
Clear |
O(1) |
d.clear() |
Removes all key/value pairs from d. |
Dictionary Copy |
O(n) |
d.copy() |
Returns a shallow copy of d. |

Fig. 6: Dictionary Operations¶
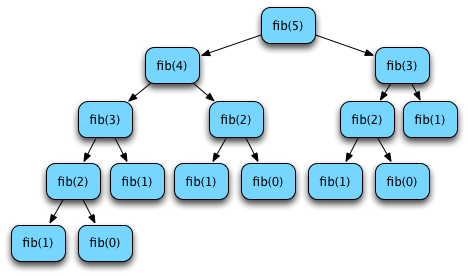
Fig. 7: Computing fib(5)¶